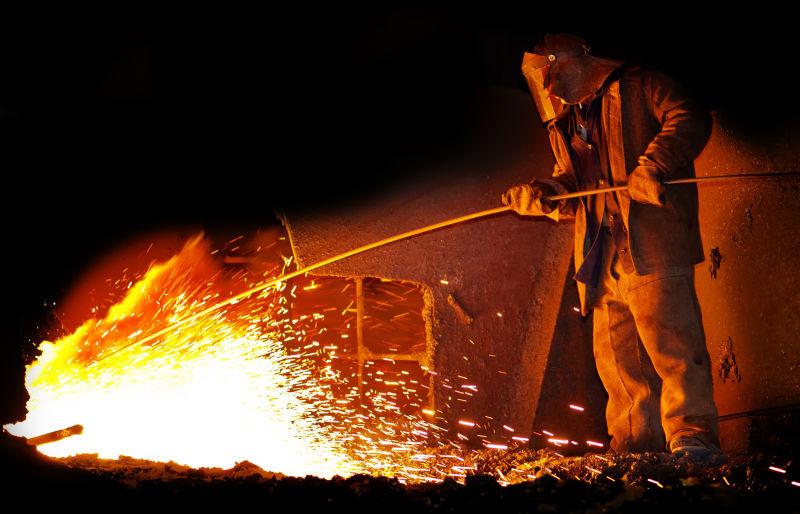
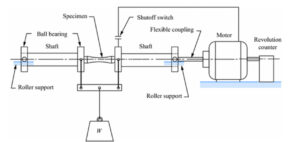
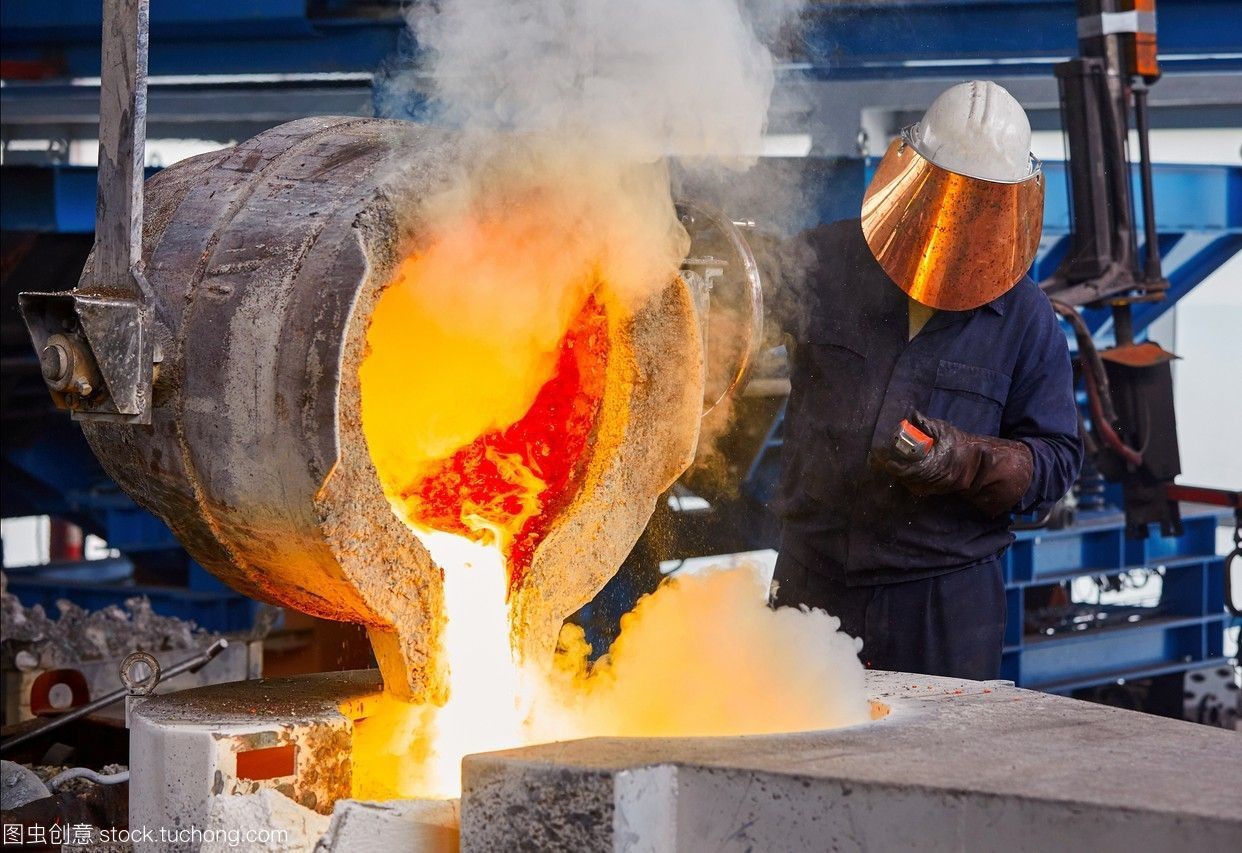
The most important step of copper bushings before casting is smelting copper alloy material. It refers to the melting of copper and other auxiliary metal materials such as zinc, tin, aluminum, and iron into liquid through a smelting furnace and tempering.
The copper alloy charge undergoes certain physical and chemical changes in the smelting furnace at about 1300°C, and the output of crude metal or metal enrichment and slag pyrometallurgical process, is one of the casting production processes of copper alloy products, with the meaning of melting and refining.
Classification of copper smelting furnace
Now the productivity of copper smelting furnaces is very high, the production capacity of a single smelting furnace is very large, and those per square meter smelting pool of day and night production capacity of several tons or even dozens of tons of copper alloy. Commonly used smelting furnaces are blast furnaces, reflection furnaces, electric furnaces, flash furnaces, converters, short kilns, new melting pool smelting furnaces, etc. Smelting equipment has been large-scale, and the process has begun to use computer control.
- The equipment used is divided into blast furnace smelting, reflection furnace smelting, electric furnace smelting (Jiaerda Machinery smelting copper alloy with the electric furnace)
- The characteristics of the process are divided into flash smelting, molten pool smelting, vortex smelting, oxygen-rich smelting, hot air smelting, matte-making smelting, and direct smelting of sulfide concentrate, and self-heating smelting of sulfide concentrate.
- According to the essence of the process reaction can be divided into oxidation smelting, reduction smelting, reduction sulfide smelting, volatilization smelting, precipitation smelting, reaction smelting, etc.
The deoxidation step in the copper smelting process
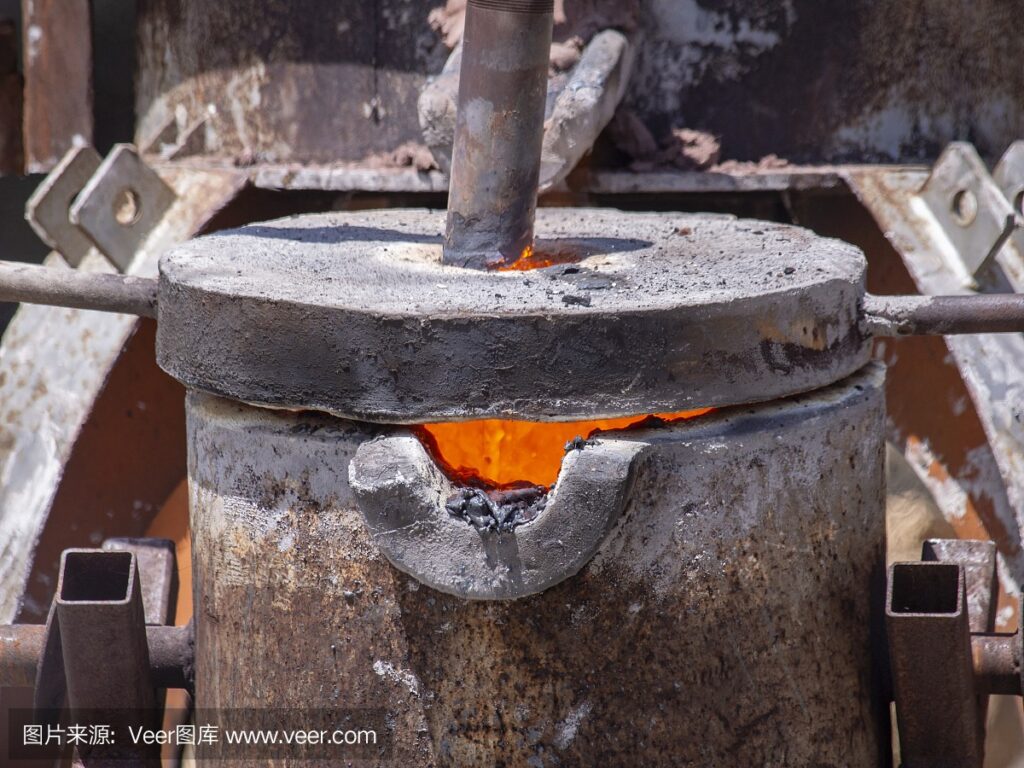



The process of reducing the oxide in the molten copper alloy to remove oxygen is called deoxidation. The process of deoxidation of copper alloy melt is a replacement reaction process. Deoxidation is carried out with the help of deoxidizing agents, which are divided into two categories for copper: surface deoxidizers and deoxidizers dissolved in the metal.
The deoxidation process belongs to the replacement reaction process, copper smelting deoxidation methods such as diffusion deoxidation, precipitation deoxidation, and composite deoxidation.
Diffusion deoxidation
The surface deoxidizer of diffusion deoxidation is not dissolved in the copper liquid, and the deoxidation reaction is mainly carried out on the surface of the smelting furnace. And the deoxidation of the melt inside the smelting furnace is mainly realized by the role of continuous diffusion of cuprous oxide to the surface of the smelting furnace.
One is because the specific gravity of cuprous oxide is smaller than that of copper, it can float to the surface of the smelting furnace.
Secondly, because the deoxidation reaction is carried out on the surface of the smelting furnace, the cuprous oxide on the surface of the copper alloy melt is continuously reduced and its concentration is continuously reduced. Because of the concentration difference, the cuprous oxide deep in the smelting furnace is constantly floating up. The rate of surface deoxidation is slow, and it takes a long time to reach complete deoxidation.
Since the deoxidation reaction takes place only at the surface, the melt inside the copper smelting furnace is not contaminated. Commonly used surface deoxidation agent in addition to charcoal, but also can use certain density is much smaller than the copper can reduce cuprous oxide solvent, such as magnesium boride (Mg3B2), calcium carbide (CaC2), boron slag (Na2B4o6-MgO), etc.

Precipitation deoxygenation
Precipitation deoxidation dissolved in the metal deoxidant can be throughout the copper smelting furnace and molten metal slag oxide interaction, deoxidation effect is much more significant.
The disadvantage is that the remaining deoxidizer will form inclusions, affecting the performance of the metal. Copper and copper alloys commonly used as such deoxidizers are phosphorus, silicon, manganese, aluminum, magnesium, calcium, titanium, lithium, etc. These metals are added in the form of pure metal or intermediate alloy, deoxidation results in the formation of gaseous, liquid, or solid products. The deoxidation reaction produces fine solid copper oxides that increase the viscosity of the metal or become unevenly distributed inclusions in the copper bushing. When using this type of deoxidizer, the amount added should be controlled.
The two deoxidation methods have their advantages and disadvantages, production can be used in a comprehensive deoxidation method. For example, when smelting oxygen-free copper with a low-frequency induction furnace, first cover with a back layer of charcoal for surface deoxidation, and then add phosphorus copper for internal deoxidation of the smelting furnace.
Environmental issues of copper-smelting
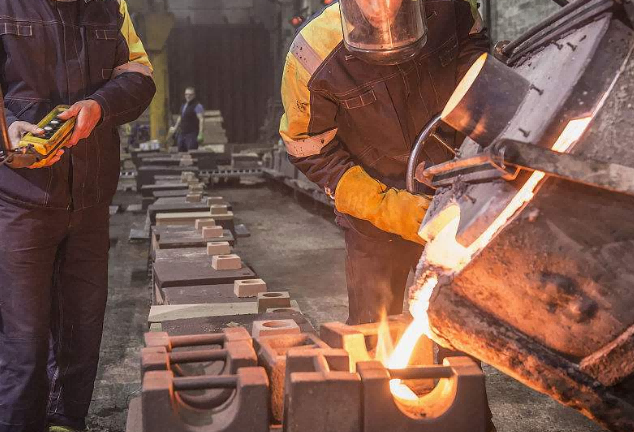


Scrap slag
Non-ferrous metal slag is a kind of iron silicate (2FeO-SiO2 ) based oxide melt, mainly composed of a FeO – SiO2 – CaO ternary system, accounting for about 80% to 90% of the total slag. It needs to be recovered separately for harmless treatment.
SO2 high-temperature flue gas
SO2 high-temperature flue gas entrained soot to be collected by a variety of dust collection equipment to improve the overall utilization of raw materials and reduce the pollution of the environment. But high-temperature flue gas also has an advantage, it is a secondary heat source, available boiler waste heat, or other heat exchange equipment to recover to produce steam or for other purposes.
The difference between a smelting furnace and a melting furnace
The difference between the two is one is “smelting” and one is “melting”. Smelting furnaces are used in the copper alloy industry.
Smelting furnace
(chemical change + physical change: melting + smelting, including metallurgical reactions) usually refers to the metal or non-metal smelting, adjusting its composition, slagging, deoxidation, degassing, and debris removal, to obtain the set composition of the industrial furnace.
Melting furnace
(physical change, solid state – liquid state), on the other hand, refers to an industrial furnace that melts metals or non-metals into liquids.
Safety matters in copper smelting



Safety production is a basic requirement of the copper alloy casting industry, pure copper and copper smelting must do the following requirements.
- Operators should wear protective equipment, work site to maintain neat, no water and debris;
- Before starting the furnace should check whether the equipment used is intact, if there are unsafe factors should be promptly removed;
- It should be carefully checked and confirmed that there are no explosive and dangerous substances in the furnace material before preheating:
- The remaining copper alloy melt after casting should be poured into the preheated ingot mold, and then poured on the ground or poured back into the furnace.
Copper smelting should pay attention to several issues
Smelting time
From the copper alloy charging, the start of smelting to the end of smelting, the time used is called smelting time. The length of smelting time will not only affect productivity, and will obviously affect the quality of the cast copper bushings finished products.
The growth of smelting time will increase the elemental burn rate of the alloy and increase the chance of gas absorption. Therefore, smelting should be completed in the shortest possible time. The preheating temperature of the furnace charge should be increased as much as possible when allowed, and the operation should be compact and fast.
The stirring bar for smelting
Some elements in copper alloys, such as Fe, Al, etc., are present in the form of mechanical mixtures during smelting. There are also some elements that have a tendency to produce specific gravity bias stratification due to different densities (Pb).



It has been proved that these elements in the process of smelting and casting are prone to cause chemical composition failure, which eventually leads to unqualified mechanical properties of copper bushings.
To overcome this phenomenon, it is necessary to resort to stirring, which is an indispensable part of smelting and casting. However, during temperature measurement and cooling, stirring is generally not required. And the material composition of the stirring bar used, it is generally appropriate to use graphite. This is because
- If other stirring materials are used, such as iron bars, the iron bars melt during the stirring process, so that the chemical composition of the copper alloy is affected.
- If the iron bar is preheated in the smelting furnace at a higher temperature or stirred for a longer period of time, the oxides on the iron bar will enter the copper alloy liquid and become impurities.
- If the preheating temperature of the iron bar is low, the copper alloy will be adsorbed on the iron bar during stirring, which can also be observed in the production.
Covering agent used in smelting

For smelting copper alloy, the amount of covering agent is generally: 0.8%-1.2% of the weight of the charge, because to maintain the thickness of the covering layer of 10-15mm; with charcoal, the amount of 0.5%-.0.7% of the weight of the charge, to maintain the thickness of the covering layer of 25-35mm covering agent picking, generally before casting, too early to carry out will increase the oxidation of copper alloy and gas absorption. If charcoal is used as a covering agent, the slag blocking effect is good, you can also not pick up the covering agent, let it also play a slag blocking role in the process of casting, and the effect is more desirable.
not in the smelting furnace copper liquid surface sampling for performance testing
Copper alloy is easy to oxidation and gas absorption, its liquid surface dross, gas content are significantly higher than the lower copper liquid; moreover, some copper alloys such as aluminum bronze, and lead bronze easy to bias, resulting in the upper part of the copper alloy liquid is less dense aluminum content, while the lower part is more lead amount. So sampling on the surface of the copper liquid makes the performance test very inaccurate.
The correct sampling should be done after fully stirring the copper liquid, and then using a sampling spoon to scoop the copper alloy liquid from the bottom of the furnace upwards.
Can I melt the copper myself?




You can use a small induction furnace to heat molten copper. Induction furnaces are furnaces that use electric current induction to generate heat to heat and melt copper materials. Furnaces are constructed in two types: core and coreless.
- In a coreless induction furnace, the copper charge in the crucible is subjected to an alternating magnetic field that generates an induction current and consequently generates heat, which melts itself and superheats the copper solution.
- In a cored induction furnace, the molten copper is added and the alternating magnetic field generated in the toroidal core superheats the copper in the trench and heats the entire copper by circulating the copper in the trench with the copper in the melt pool above it.
Note: The coreless induction furnace has the ability to melt the solid charge, while the cored induction furnace can only superheat the molten iron, but in terms of superheating the copper liquid, the power consumption is more economical with the cored induction furnace.
The following points should be noted when using:
- Before starting the operation should first observe the power supply voltage value and power balance;
- Carefully check the connection of the electrical contacts, especially the silicon-controlled pile, electric heating capacitors, water-cooled cables, etc.;
- Open the cooling circulating water system to check the operation of the main body, the water circuit of the furnace and maintain a certain water pressure;
- Furnace lining sintering and baking in order to reduce the role of electromagnetic stirring on the erosion of the furnace lining, to run at low power (reduce voltage) for a period of time, so that the furnace body evenly warming;
- In normal operation, should also be more patrol equipment operation, especially the water temperature of each branch, experienced people even by the sound of the change to determine whether the equipment is normal;
- Electric furnace interruption, the cooling water can be properly reduced, but can not turn off the cooling water, otherwise, the residual heat of the furnace lining will burn the coil and insulation layer.
Off-topic of copper smelting slags
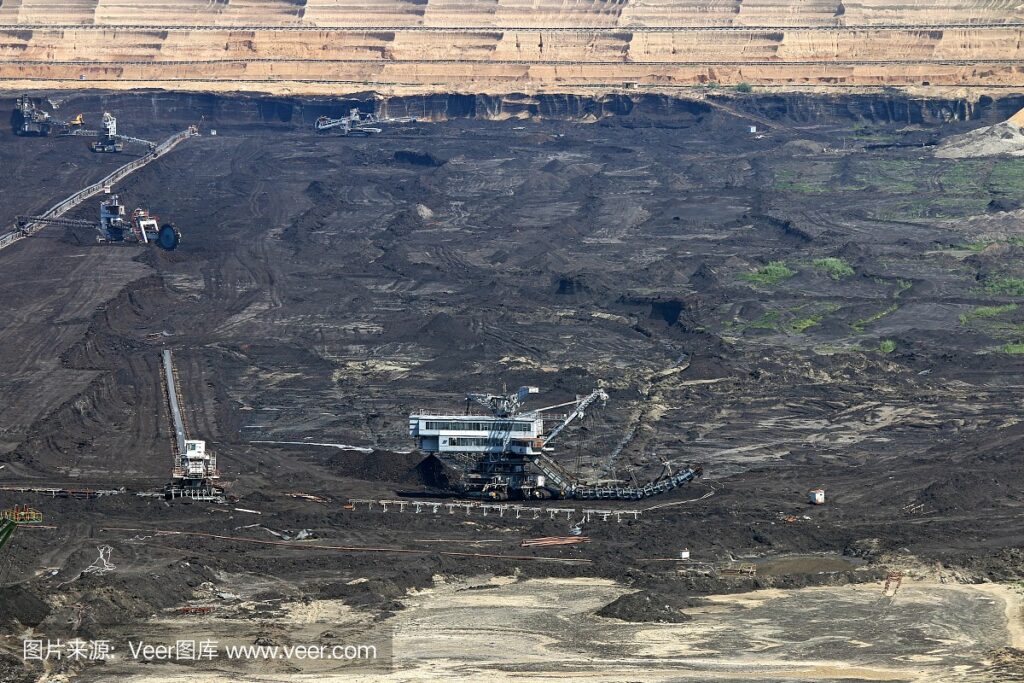

As we all know, copper smelting is the first step in the production of copper alloys products. Electrolytic refining of large quantities of copper ores/copper minerals to get pure copper, early copper smelting/primary copper smelting to get liquid copper, copper scrap, and copper smelting slag is a large industrial scale.
Every copper bushing factory attaches great importance to the smelting process of copper alloys, including copper bushing casting is considered to be the core of the two technologies of copper bushing factory.
Cathode copper, metallic copper, copper compounds, precious metals, blister copper, copper metallurgy, liquid metal, copper concentrates, and other related metallic copper production knowledge, the factory requires some theoretical training before the staff can start work.



How to solve the raw material, earth has large quantities of iron ore, copper deposits mountain range, extractive metallurgy experience, and smelting technology is also very advanced. This raw material of molten lead, arsenic bronze, non-ferrous metals, nobel metals, and precious metals will be made into metal artefacts in part after reasonable compliance with environmentally friendly smelting, and we can also see a part of the final bronze left in some programs explaining the middle Bronze Age.
After extracting copper ores, smelters of a certain industrial scale will continue to further processing, using high-temperature furnaces (shaft furnace, anode furnaces, etc.) to remove impurity elements, converter slag, and obtain other metals such as alloying elements. This involves a molten bath, solvent extraction, carbon monoxide removal, and other technologe.
It is also necessary to test slag sample from copper smelting. Early metallurgy has the knowledge of modules including co-smelting, elemental composition, reduction processes, chemical reactions, flue dusts, metallurgical processes, anode slimes, main material, etc. The latest metallurgy is subdivided into new processes, phase compositions, the preliminary elemental composition obtained by scanning electron microscope and then continues with the study of the elemental composition and chemical reactions of reduced copper and copper alloys.