Heat hazard simply means: that our human body will be affected by health because of being in a hot environment for a long time. heat-related illnesses such as heat syncope, heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heat stroke, and even more serious conditions can occur if you live and work in the heat and hot environments for a long time.

Preventing heat hazard in bronze bushing smelting shops
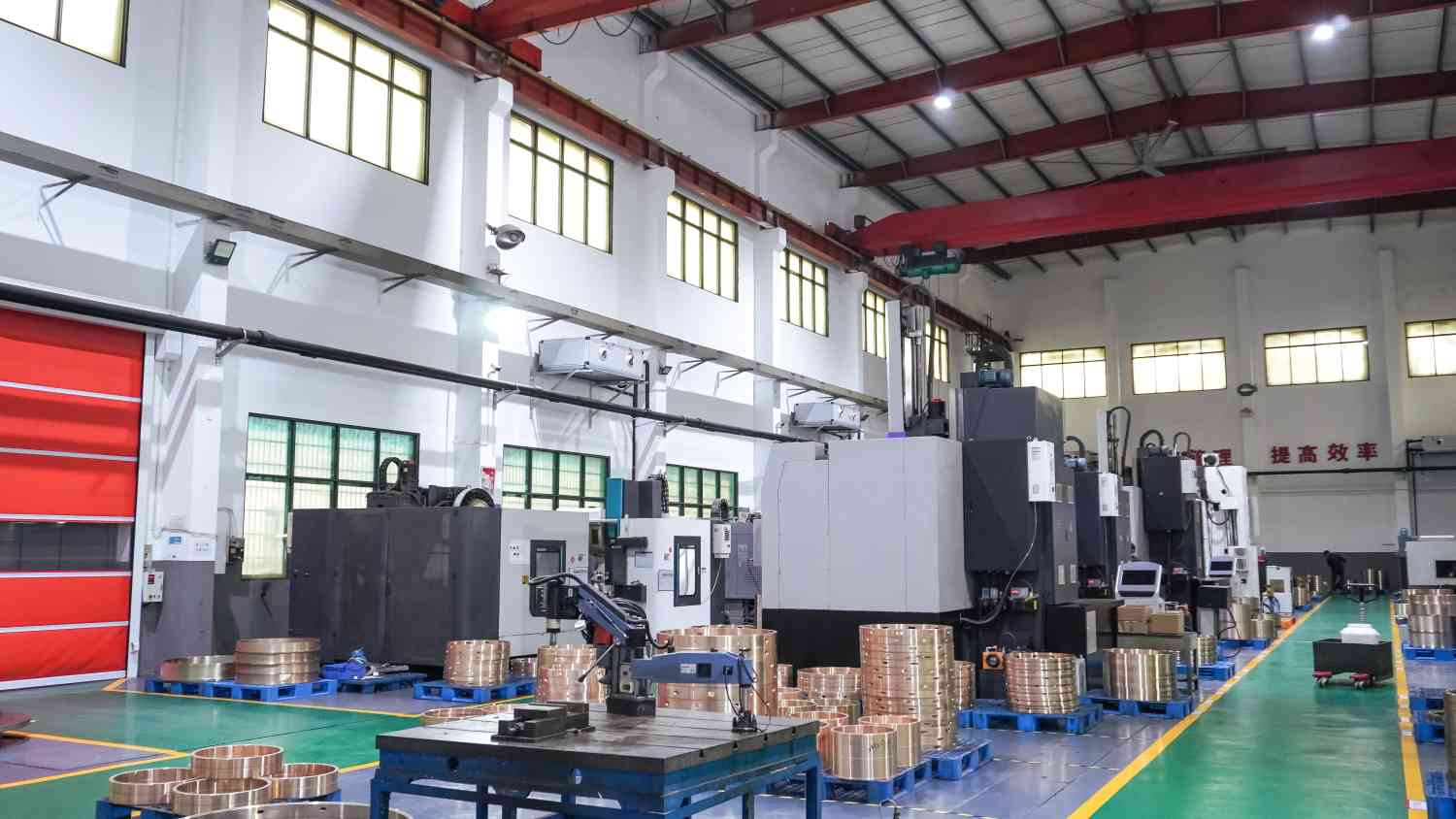
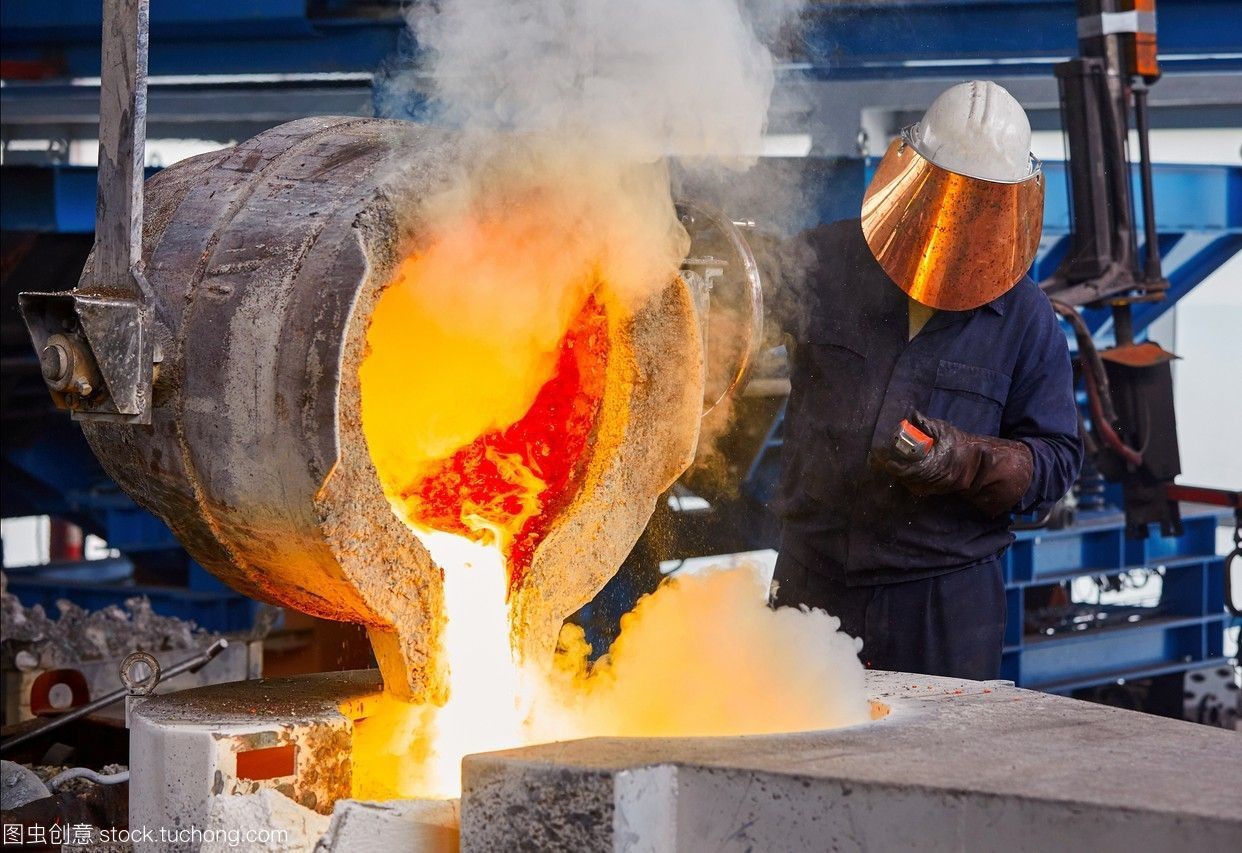
The first and most important step in the production of bronze bushings is smelting. We have a 24-hour smelting line with a total of 10 high-temperature smelting furnaces. In order to avoid heat hazards that may occur in the operation and cause heat-related diseases. We have made a series of health management and occupational safety measures.
The air temperature and relative humidity of the workshop are monitored 24 hours a day.
When you suddenly enter an environment where high temperatures are obvious, you immediately perceive the danger. But if you are in an environment with a critical point of high temperature for a long time, you will be paralyzed, so a high-temperature alarm is needed to indicate the danger.
24-hour supply of cool water.
Not only is cool water available, but you must wear fogged safety glasses, safety clothing, gloves, and other personal protective equipment to prevent burns from copper alloy liquids while working.
24-hour medical workshop(occupational safety)
Provide occupational safety and health management, labor statistics, occupational safety, and health inspection, disease prevention, heat stroke medicine, hypertension measurement, etc.
6-hour shift work system.
Control working hours, and shift change to check body temperature and check for broken personal protective equipment.
What are the work environments prone to heat hazards

High temperature and strong radiation
- metallurgical industry’s coking, iron making, steel making, and steel rolling room.
- Casting, forging, heat treatment, and other shifts in the machinery manufacturing industry.
- Furnace and kiln shifts in the ceramic, brick, and tile industries.
- Thermal power plants and boilers on ships such production sites have a variety of different heat sources, such as smelting furnaces, heating furnaces, kilns, boilers, heated objects (iron, steel, ingots), etc., can be made by conduction, convection, radiation heat dissipation, so that the surrounding objects and air temperature increases.
After the surrounding objects are heated and can become a secondary source of heat radiation, and due to the expansion of the thermal radiation surface, the temperature is higher, in this type of operating environment, there are two different natures of heat, namely convection heat (heated air) and radiation heat (heat and secondary heat sources).
Convective heat only acts on the surface of the human body, but heats the whole body through blood circulation; radiant heat acts on the surface of the human body, but also on the deep tissues, so the heating effect is faster and stronger.
The meteorological characteristics of such operations are high temperature, high intensity of heat radiation, and low relative humidity, forming a dry and hot environment, people will sweat a lot when working in this environment, such as poor ventilation, it is difficult to evaporate sweat, it may be difficult to evaporate heat dissipation and heat storage and overheating.
High temperature and high humidity work


Characterized by high temperature and humidity, while the intensity of radiation is not large. The formation of high humidity is mainly due to the production process producing a large amount of water vapor heavy, the production process requires the shift to maintain a high relative humidity caused.
- Printing and dyeing, the United States; silk, paper, and other industries in the liquid heating or steaming, the shift temperature up to 35 ℃ or more, the relative humidity is often up to 90% or more.
- The humid prospecting shaft inside the temperature can reach more than 30 ℃, relative humidity can reach more than 95%, such as poor ventilation will form a high temperature, high humidity, and low airflow of adverse weather conditions, that is, hot and humid environment.
People work in this environment, even if the temperature is not very high, but due to the evaporation of heat dissipation is extremely difficult, although a lot of sweating can not play an effective heat dissipation, easy to lead to heat accumulation in the body or water, electrolyte balance imbalance, thus sending heat stroke.
- Summer open-air work.
Construction, handling, and other operations of high temperature and heat radiation is the main source of solar radiation.
Summer open-air operations are also subject to the additional heat of the ground and the secondary source of radiation from surrounding objects. Although the intensity of heat radiation in open-air work is lower than in high-temperature shifts, the duration of its effect is longer, and the head is often exposed to direct sunlight, coupled with the rise in temperature around noon, at this time, such as labor intensity is too high, the human body is very easy to heat stroke due to excessive heat storage.
The impact of thermal hazards


High temperature can cause a series of changes in the physiological functions of the workers, mainly as follows.
- In thermoregulation disorders, due to heat storage in the body, body temperature increases.
- A large amount of saline loss can cause disorders in the balance of water and salt metabolism, resulting in an imbalance of acid-base balance and osmotic pressure in the body.
- Accelerated heart rhythm and pulse, increased skin vasodilation and vascular tension increased heart burden, and decreased blood pressure. However, blood pressure may also increase during heavy physical work.
- Anemia of the digestive tract reduced the secretion of saliva and gastric juice, decreased acidity of gastric juice, decreased starch activity – slowed gastrointestinal motility, resulting in indigestion and other gastrointestinal disorders.
- An insufficient supply of water and salt under high-temperature conditions can concentrate urine and increase the burden on the kidneys, sometimes leading to renal insufficiency and the appearance of protein and red blood cells in the urine.
- The nervous system may show central nervous system inhibition, concentration, muscle work ability, accuracy and coordination of movement and reaction speed reduction, etc.
- An acute disease occurring in a high-temperature environment is heat stroke, which can be classified as pyrexia, sunstroke, heat exhaustion, and heat cramps according to the pathogenesis. In order to make it easy for enterprises to identify in the registration and reporting of occupational diseases, heat stroke is divided into the following three types in the “Interim Measures for Heat Stroke Prevention and Cooling”.
- Aura heat stroke. In the process of high-temperature work dizziness, headache, eye blossoms, ear ulcers, palpitations, nausea, weakness of the limbs, inattention, uncoordinated movements, and other symptoms, body temperature is normal or slightly elevated, but still able to hold on to work.
- Mild heat stroke. With the aforementioned symptoms, and once forced to stop working, but after a short rest, the symptoms disappear and can resume work.
- Severe heat stroke. With the aforementioned symptoms of heat stroke, forced to stop working, or suddenly fainted at work, dry skin without sweating, body temperature above 40 ℃, or heat cramps.
Heat stroke prevention and cooling measures

Relocation:
Reasonable arrangement of heat sources within the hot shift to avoid heat source action around the operator. If the heat source cannot be moved, heat insulation measures should be taken.
Air ventilation
An important measure to prevent heat and cool down, natural ventilation should be strengthened, so that high temperature in the shift is discharged from high windows or air holes. A wind cap can be installed on the roof of the team, and windows can be opened in the corners to strengthen ventilation. When natural ventilation can not discharge all the residual heat, mechanical ventilation should be used.
PPE
Strengthen individual protection. High-temperature workers should wear light-colored work clothes with heat resistance, sturdiness, small thermal conductivity, and good ventilation function, and gloves, shoe covers, leg protectors, glasses, face masks, work caps, etc. according to the protection needs.
Rotation
Develop a labor and rest system, adjust work and rest time, and adopt a multi-shift working method; reasonably arrange resting places between jobs.
air conditioning room
set up an air-conditioned restroom near the workplace. Employees can cool down their body temperature.
Heat stress is a change in the temperature of the object or uneven distribution is the stress generated inside the object. Extreme heat environments can cause heat-related illnesses. Heat stress also requires knowledge of core body temperature, excess heat, heat index, heat exposure, metabolic heat, etc.
Insights related to heat stress
This year’s summer has been very hot and the National Weather Service is advising the public to do their health administration, prevent heat-related illness against diseases and stay away from radiant heat sources. Heat rashes, prickly heat, and other heat-related hazards.
For outdoor workers, you need to drink more water during strenuous physical activity and do not enter an air conditioning room immediately after excessive sweating. It is best to establish a system of a buddy system for safety and health administration.
For smelting and foundry shops, we organize personnel to learn about heat stress, heat illness, environmental and metabolic heat, excess heat, heat index of hot environments, heat exposure, and heat-related illnesses.



Protecting workers is the first element of a smelting shop. Check the equipment, to replace the fogged-up safety glasses, and 24-hour environmental heat measurements. Heat stress disorders investigation, metabolic heat, wet bulb globe temperature, and heat rash, all must be strictly regulated by safety regulations.
Illness prevention in high-temperature environment and prevent heat illness are also important matters. They generally include actual air temperature, heat strain, hot surfaces, environmental heat, total heat stress, heat illnesses, and intensity of direct sunlight exposure.
Companies also need to focus on occupational health management of employees and do a good job hazard analysis including total heat stress experienced by the environment, hot air, heat exchange, body’s ability, high blood pressure, risk of heat, and serious illness.
Physical labor requires drink water and replenishing electrolytes. Avoid heat injury, and heat exposures, be aware of air movement, and core temperature of hot objects, know the symptoms of heat and the risk of heat related, and take safety measures when workers exposed to hot objects.