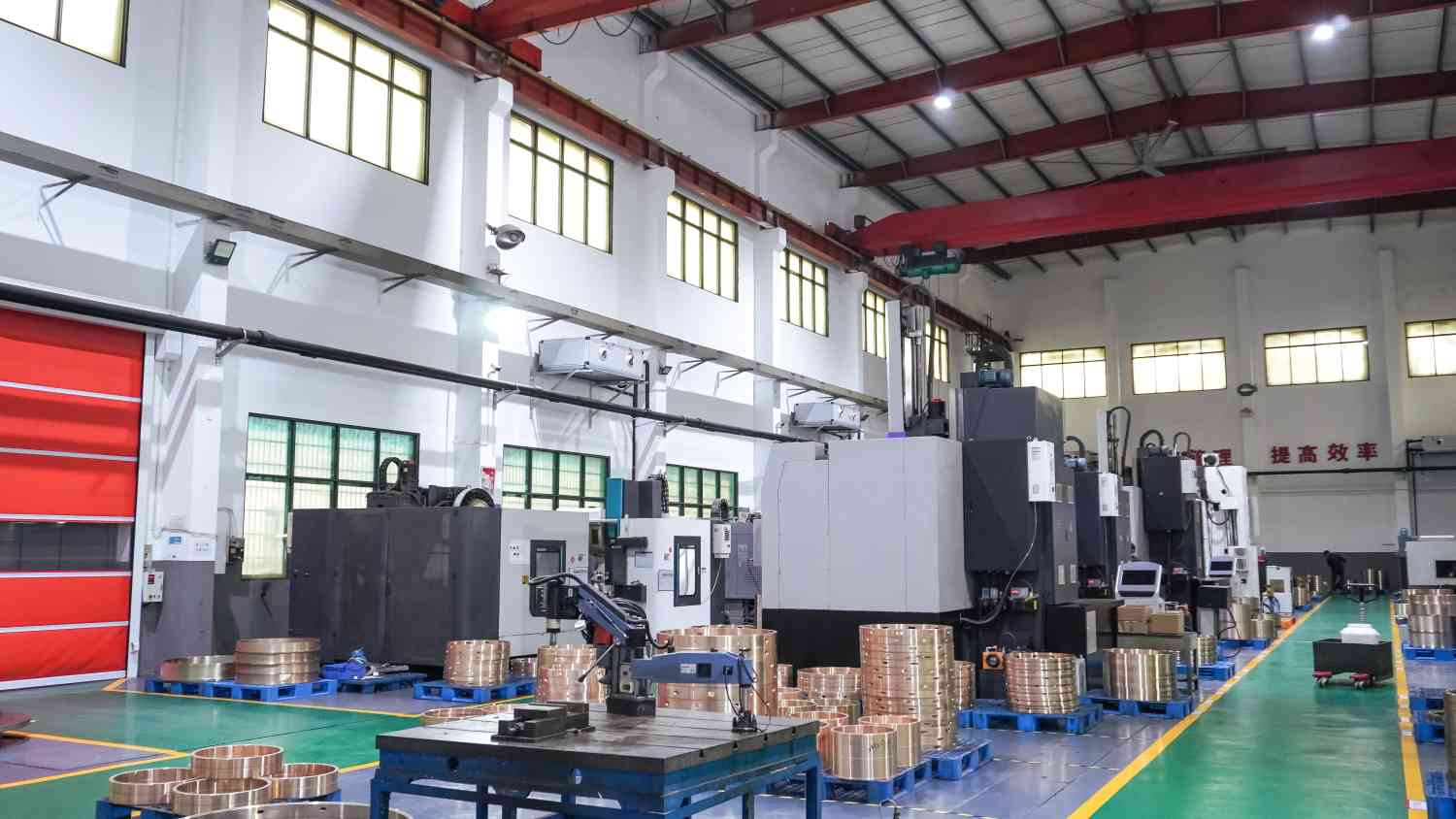
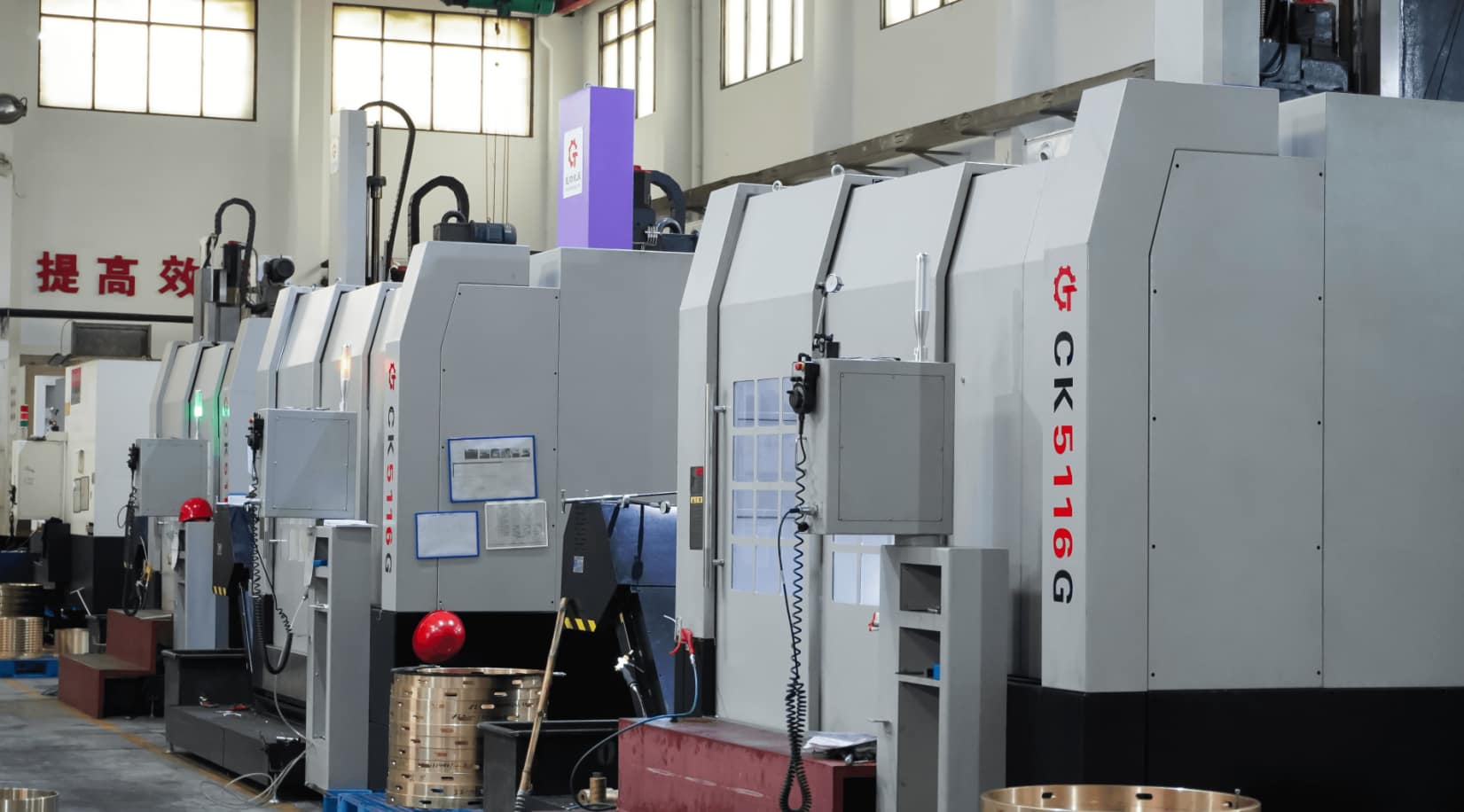
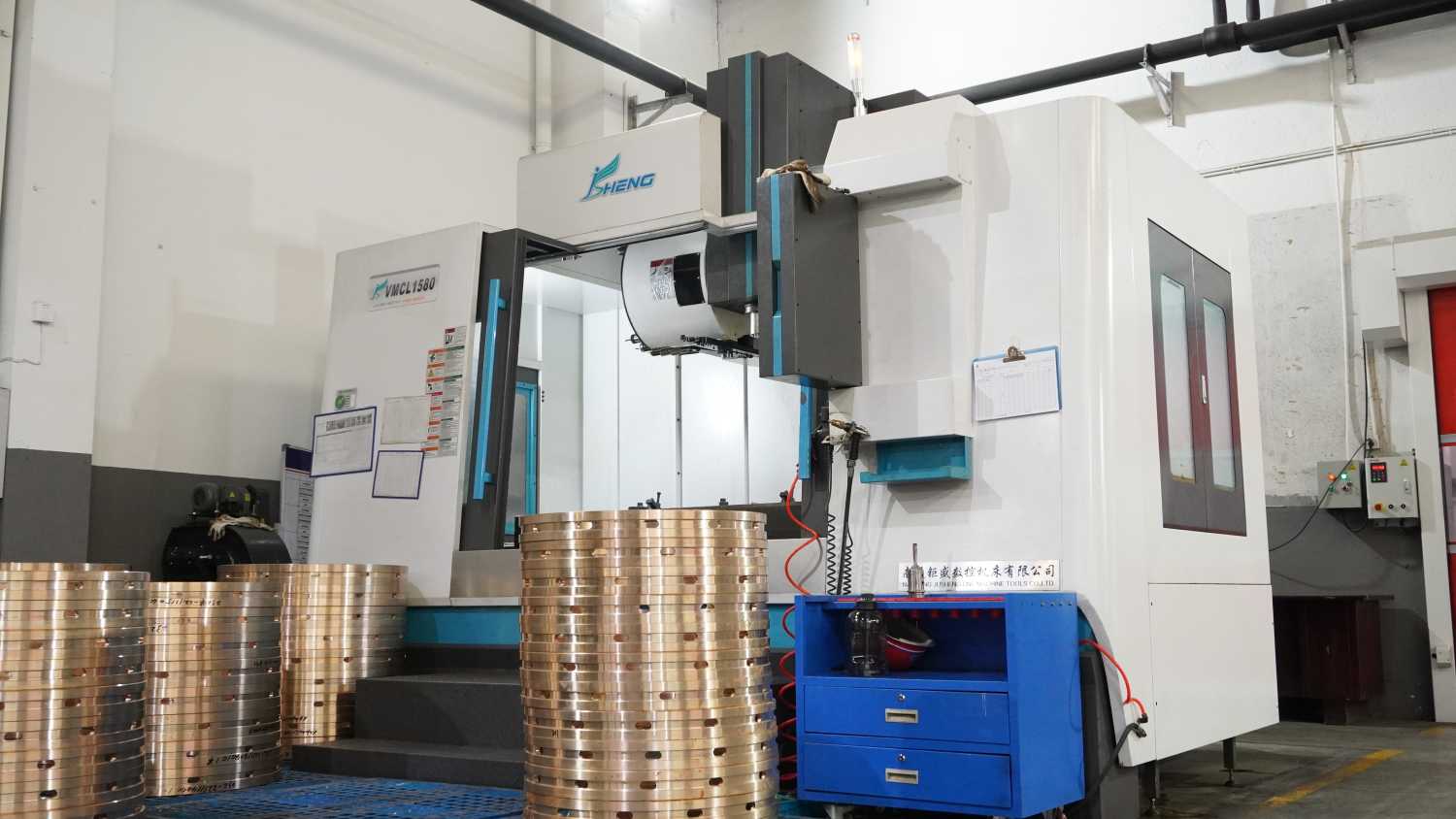
The wind turbine gearbox is the transmission part connecting the main shaft of the wind turbine and the generator. Its main function is to transform the low-speed running input of the main shaft into the output required by the medium-speed or high-speed generator, which is one of the important parts of wind turbines.
Due to the complex working conditions of wind turbine systems and the high requirements for reliability, the design and application of wind turbine gearboxes, especially the selection, installation, and use of bearings as key components, are particularly important.

Which bronze bushings do you have for wind power generation?
We focus on the development and manufacture of bronze rings for wind turbine systems and have a special bronze bushing production line for wind turbine systems.
Our floating mating bronze oil rings, bronze oil seals, and bronze rings are used in 1.5MW, 1.65MW, 2MW, 2.5MW, 2.75MW, 3MW, 3.5MW, 4MW, 5MW, 6MW, and 7MW wind turbine gearboxes.
Bronze oil seal, bronze floating oil ring, bronze ring, and gearbox bronze ring are mainly made of tin bronze CuSn10p1 (C90710): high hardness, good wear resistance, not easy to produce bite phenomenon, good casting performance and cutting performance, good corrosion resistance in the atmosphere and fresh water.
What is the role of the gearbox in a wind turbine?

The gearbox in the wind turbine is an important mechanical part, its main function is to transfer the power generated by the wind wheel under the action of wind to the generator and make it get the corresponding speed.
As the unit is installed in the wind mouth of the mountains, wilderness, beaches, islands, etc., the working environment is harsh, coupled with the natural environment in which the traffic is inconvenient, once there is a failure, it is very difficult to repair, so the reliability and service life of its various accessories, including oil seals, floating oil ring is much higher than the general mechanical requirements.
Improper bearing selection or improper installation and use will lead to various damage and failure modes of bearings, and may even damage other parts in the gearbox. These damages and failures can directly or indirectly lead to downtime, which not only affects productivity but also generates unplanned replacement and maintenance costs.
What is the bearing pressure range of a typical wind turbine gearbox?
The load capacity of bearings is divided into dynamic and static.Dynamic is assessed using the number of hours of fatigue life.
The actual assessment criteria are the result of a combination of both load and rotational speed and are not determined by load alone, so it is difficult to answer. If the speed is very low and the life requirement is not high, the load can be very large.
What are the design requirements for the wind power industry




A requirement related to wind power bearing design is that the GL standard requires the contact stress of the bearing to be less than 1500 MPa. This requirement is borrowed from the fatigue limit of ISO 281, however, it is still doubtful whether this method is reliable, because the failure form of wind power bearings, especially WEC, is not summarized in the bearing life theory.
As another example, the life calculation tool of the ASME standard is also different from ISO, where the applied fatigue limit is translated into contact stress of 1140 MPa.
As for statics, a safety factor can be used to assess this.
Maintenance of copper bushings for gearboxes?
- Tap the copper sleeve: check the wear of the copper sleeve, the bottom carbon piece more than 1/3 wear that is replaced, use the work extension screw to remove the copper cap:
- Check the wear, need to replace for new, do not need to replace re-application of lubricant. Check the front 7 after 5 a total of 12 copper sleeves.
- Knock the copper sleeve position reserved a copper sleeve is not installed, yaw 360 ° coated with yaw transparent yellow lubricant E2
- Knock the copper sleeve front side 7 positions below the oiling port to fill the lubricant.

Self-lubricating copper sleeve maintenance methods.
- In motion, if found self-lubricating copper sleeve overheating, immediately stop and check, so that the rotor continues to run at low speed, or continue to supply oil for a period of time until the copper sleeve cold down.
- To prevent the self-lubricating copper sleeve lubrication effect is poor, to prevent the oil mixed with impurities.
- Gluing damage to the lighter copper sleeve, you can use the scraping repair method to eliminate, it and continue to use it.
- To prevent bias load and overload, it is recommended that the use of suitable pasteurized alloy as well as a new bearing structure.
- The strict control of bearing temperature rise.
- Check the appearance of the self-lubricating copper sleeves whether there is wear and scratches and whether the lubricant is mixed with impurities, foreign bodies and dirt.
wind energy industry bronze bushing
In the wind turbine gearboxes, plain bearings, bronze bushing, and other bearings are called wind turbine gearbox bronze bushing (this article does not include roller bearings and lead bronze sintered bushings)
Wind turbines, wind turbine gearboxes, rotor blades, rotor hub, hollow shaft, main shaft, spindles, yaw system, plain bearing, gearboxes, etc. are all part of the wind turbine systems.
Among the universal plain bearing material, it can adapt to the wind power industry, wind energy industry, renewable energy industry, the need to test corrosion resistance, excellent wear resistance, good emergency running properties, high chemical resistance, strong alternating stresses, lower maintenance costs, long service life, heavy loads and lubrication force.



Jedbushing year plan
In our year-round production of bronze bushings and plain bearings for gearboxes, product quality is always at the top of the list. Among the top ten gearbox manufacturers in China’s wind power industry, we are the largest supplier of plain bearings, accounting for 60% of the national volume.
Renewable energy industry also includes hydroelectric power generation, thermal power generation, etc.
We have in-depth understanding of the negative impact of renewable energy industry on bearing life, low friction, tribo chemical corrosion, rotate synchronously of main shaft, hollow shaft and rotor shaft. heavy load of rotor hub, high rigidity, high rigidity, negative impact, impact resistance and other factors to meet the product requirements of turbine manufacturers.
The production of plain bearing products for this industry accounts for a large percentage of our total production. In order not to affect the production of bearings for other industries, we will develop other production lines and rearrange the supporting facilities.
Rough understanding of wind turbine systems
In most wind turbine systems and wind turbines systems, the wind turbine is the big accessory. The plain bushings range includes: plain bearings, lubricated bearing, roller bearings, lead bronze bushings, etc.
Rotor shaft twists mechanical rotary motion in the bearing position of the radial load requires good emergency running properties. Plain bearings, rotor blades, hollow shaft, also affect the generator operation. Wind power applications in the beginning also need to understand the wind direction, wind speed, micro movements, stick slip on a large scale.
The plain bearing is not connected to a metal lead and has no strained contact points. Deep understanding of the wind industry will reveal that product quality and long-life bearings, especially plain bearings, are very important and will be displayed on the design pap. Some also require steel-base bearings, which are steel and copper composite bearings(bimetal bearing).
What other bronze bushings are made besides the wind power industry?
Bronze bushings for the hydraulic industry are also a relatively large part of our industry, in addition to bronze bushings for hydroelectric units in sizes ranging from 2 to 5 meters. Mining machinery, marine vessels, etc.
We have covered 60% of the wind turbines industry nationwide with our bronze bushings/bearings, and are also opening up markets abroad, currently developing a market in Japan.